OSPF Non Broadcast Multi Access - NBMA
OSPF behaves differently while peers are connected using various kind of networks. Below are the different Network Types:
- Point to Point
- Broadcast
- Non-Broadcast Multi Access (NBMA)
- Point to Multi-point Broadcast
- Point to Multipoint Non-Broadcast
This article will discuss the details of OSPF Non-Broadcast Multi Access Network.
In OSPF Non-Broadcast Multi Access Network, OSPF runs the operation over a broadcast network. A DR and BDR are elected for the NBMA network, and the DR originates an LSA for the network. In this environment, the routers are usually fully meshed to facilitate the establishment of adjacencies among them. If the routers are not fully meshed, the DR and BDR should be selected manually using "neighbor x.x.x.x" command to ensure that the selected DR and BDR have full connectivity to all other neighbor routers. Neighboring routers are statically defined to start the DR/BDR election process.
router ospf 1
neighbor x.x.x.x (IP address of neigbhor interface)
neighbor x.x.x.x (IP address of neigbhor interface)
Use the neighbor command to statically define adjacent relationships in NBMA networks using the non-broadcast mode.
OSPF NBMA - Neighbor Command Syntax
Router(config-router)#neighbor ip-address [priority number] [poll-interval number] [cost number] [database-filter all]
Description
- ip-address: Specifies the IP address of the neighboring router.
- priority number: It is an optional field that specifies priority of neighbor. The default is 0, which means that the neighboring router does not become the DR or BDR.
- poll-interval number: It is an optional field that Specifies how long an NBMA interface waits before sending hellos to the neighbors even if the neighbor is inactive. The poll interval is defined in seconds.
- cost number: It is an optional field that Assigns a cost to the neighbor in the form of an integer from 1 to 65535. Neighbors with no specific cost configured assume the cost of the interface based on the ip ospf cost command. For point-to-multipoint interfaces, the cost keyword and the number argument are the only options that are applicable. This keyword does not apply to nonbroadcast mode.
- database-filter: all It is an optional field that filters outgoing LSAs to an OSPF neighbor.
The default priority on the neighbor command is supposed to be 0. However, during testing it was noted that configuring the priority in this way for non-broadcast mode interfaces actually resulted in a priority of 1, not 0. Setting the OSPF priority to 0 at the interface level (with the ip ospf priority command) results in a priority of 0 and the routers are not being elected as DR or BDR.
interface Serial1/0
ip ospf priority 2
High Priority should be put on DR/BDR. Spokes can be configured with 0 Priority
In Non-Broadcast Multi Access network, neighbor statements are required only on the DR and BDR. In a hub-andspoke topology, neighbor statements must be placed on the hub, which must be configured to become the DR by being assigned a higher priority. Neighbor statements are not mandatory on the spoke routers. In a full-mesh NBMA topology, you might need neighbor statements on all routers unless the DR and BDR are statically configured using the ip ospf priority command.
OSPF NBMA - Summary
- One IP subnet.
- Neighbors must be manually configured.
- DR and BDR are elected.
- DR and BDR need to have full connectivity with all other routers.
- Full- or partial-mesh topology.
Default OSPF Modes for various OSPF networks
- The default OSPF mode on a point-to-point Frame Relay subinterface is the point-to-point mode.
- The default OSPF mode on a Frame Relay multipoint subinterface is the non-broadcast mode.
- The default OSPF mode on a main Frame Relay interface is also the non-broadcast mode.
OSPF NBMA - Lab and Config
OSPF NBMA Configuration for router R1 and R2
R1
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.10.12.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf 1 area 0
no keepalive
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2016000
frame-relay map ip 10.10.12.2 200
R2
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf priority 2
ip ospf 1 area 0
no keepalive
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2016000
frame-relay map ip 10.10.12.1 200
router ospf 1
neighbor 10.10.12.1
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.10.12.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf 1 area 0
no keepalive
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2016000
frame-relay map ip 10.10.12.2 200
R2
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf priority 2
ip ospf 1 area 0
no keepalive
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2016000
frame-relay map ip 10.10.12.1 200
router ospf 1
neighbor 10.10.12.1
Specifically on R2, OSPF priority has been increased from 1 (default) to 2 so that it always get elected as a DR. R1 is elected as BDR because its priority is 1.
R1#show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Lo0 1 0 10.10.0.1/32 1 LOOP 0/0
Se1/0 1 0 10.10.12.1/24 64 BDR 1/1
R1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.10.0.2 2 FULL/DR 00:01:57 10.10.12.2 Serial1/0
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Lo0 1 0 10.10.0.1/32 1 LOOP 0/0
Se1/0 1 0 10.10.12.1/24 64 BDR 1/1
R1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.10.0.2 2 FULL/DR 00:01:57 10.10.12.2 Serial1/0
OSPF NBMA - Hello and Holddown Timers
Dead and Hello timers changes from default values of 10/40 to 30/120 for NBMA network.
R1#show ip ospf interface s1/0
Serial1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.10.12.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.10.0.1, Network Type NON_BROADCAST, Cost: 64
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 64 no no Base
Enabled by interface config, including secondary ip addresses
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 10.10.0.2, Interface address 10.10.12.2
Backup Designated router (ID) 10.10.0.1, Interface address 10.10.12.1
Timer intervals configured, Hello 30, Dead 120, Wait 120, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 120
Hello due in 00:00:13
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 10.10.0.2 (Designated Router)
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)stEthernet0/0
Route metric is 20, traffic share count is 1
Serial1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.10.12.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.10.0.1, Network Type NON_BROADCAST, Cost: 64
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 64 no no Base
Enabled by interface config, including secondary ip addresses
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 10.10.0.2, Interface address 10.10.12.2
Backup Designated router (ID) 10.10.0.1, Interface address 10.10.12.1
Timer intervals configured, Hello 30, Dead 120, Wait 120, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 120
Hello due in 00:00:13
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 10.10.0.2 (Designated Router)
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)stEthernet0/0
Route metric is 20, traffic share count is 1
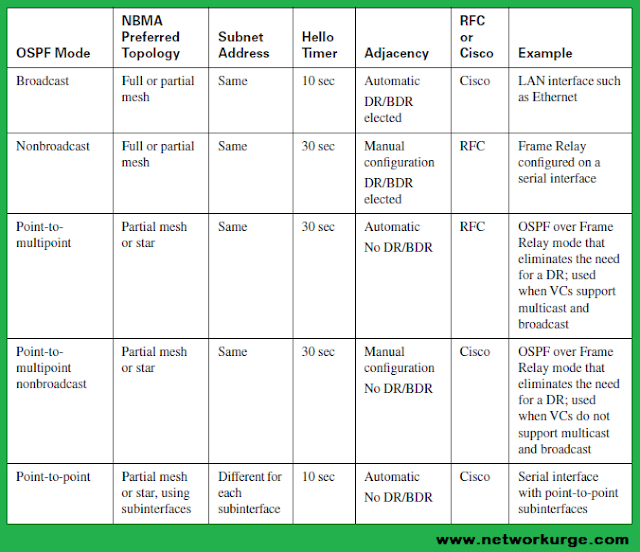
Below is the description of varios OSPF networks and related parameters.
I hope
you have found this article informative and useful and now have a fair
understanding of the OSPF Non-Broadcast Multi Access Network Concept. For any of the related queries or feedback,
kindly
write to us at networkurge@gmail.com